イムノアッセイにおけるアニマルフリー化や動物を用いないイムノテクノロジーについての記事をこちらに掲載します。
今や、免疫動物を利用しないAnimal Free Technologyは大手製薬企業を始めとして世界的な動きとなっています。日本もこの波に乗り遅れることがないように対応を急ぐ必要があります。
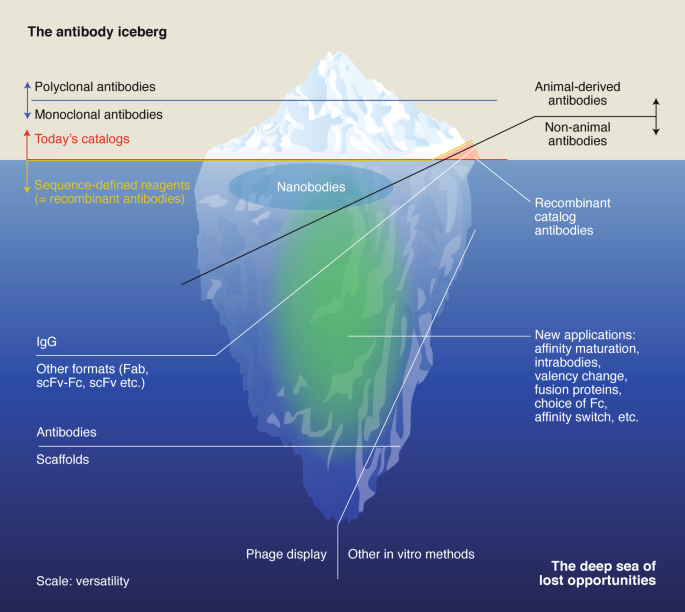
Animal-free alternatives and the antibody iceberg
Nature Biotechnology volume 38, pages 1234–1239 (2020)
以下、動物倫理の部分を抜粋。
Motivated by the scientific and ethical issues posed by animal-derived antibodies — and European Union (EU) Directive 2010/63/EU3, which requires the use of animal-free replacement methods if available and scientifically justified — the EU Reference Laboratory for Alternatives to Animal Testing (EURL ECVAM) convened a scientific advisory committee (ESAC) working group to “review the scientific validity of non-animal-derived antibodies and non-antibody affinity reagents used for research, regulatory applications and diagnostics.” At the request of ECVAM, the ESAC excluded from its analysis any antibodies to be administered to human patients. The ESAC notes that the generation of antibodies from universal libraries or from immunized animals (including transgenic animals), converted into recombinant format, are both well established for therapeutic uses. The report concluded “that non-animal derived antibodies are mature reagents generated by a proven technology that are not only equivalent to animal-derived antibodies, but in many respects can offer significant scientific advantages and economic benefits.” The EURL ECVAM released its recommendation on non-animal-derived antibodies in May4. Collectively, the ESAC report and opinion, as well as the EURL ECVAM recommendation, form the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre (JRC) science-for-policy report. Even though the ESAC review did not cover the field of therapeutic applications, the EURL ECVAM recommendation considers non-animal-derived antibodies to be a suitable alternative in this field as well, in accordance with the directive.(一部抜粋)
動物由来の抗体によって引き起こされる科学的および倫理的問題 — 欧州連合 (EU) 方針 2010/63/EU3 によって動機付けられました。 動物実験代替法 (EURL ECVAM) は、科学諮問委員会 (ESAC) ワーキング グループを召集し、「研究、規制アプリケーション、および診断に使用される非動物由来抗体および非抗体親和性試薬の科学的妥当性を検討する」ことを目的としました。 ECVAM の要請により、ESAC はヒト患者に投与される抗体を分析から除外しました。 ESAC は、ユニバーサル ライブラリーまたは免疫化された動物 (トランスジェニック動物を含む) からの抗体の生成を組換え形式に変換することは、どちらも治療用途で十分に確立されていることに注目しています。 報告書は、「非動物由来の抗体は、動物由来の抗体と同等であるだけでなく、多くの点で重要な科学的利点と経済的利益を提供できる、実証済みの技術によって生成された成熟した試薬である」と結論付けています。 EURL ECVAM は、5 月 4 日に非動物由来抗体に関する勧告を発表しました。 ESAC の報告書と意見、および EURL ECVAM の勧告をまとめて、欧州委員会の共同研究センター (JRC) の政策科学に関する報告書が形成されます。 ESAC のレビューは治療用途の分野をカバーしていませんでしたが、EURL ECVAM の勧告では、指令に従って、この分野でも非動物由来の抗体が適切な代替物であると見なされています。(一部抜粋し、Google翻訳)
Physicians committee for responsible medicineの提言
Animal- versus in vitro-derived antibodies: avoiding the extremes
Merck社の取り組み
Biorad社の取り組み